2.9 KiB
2.9 KiB
orx-easing
Easing functions for smooth animation or non-linear interpolation.
Similar to those on https://easings.net
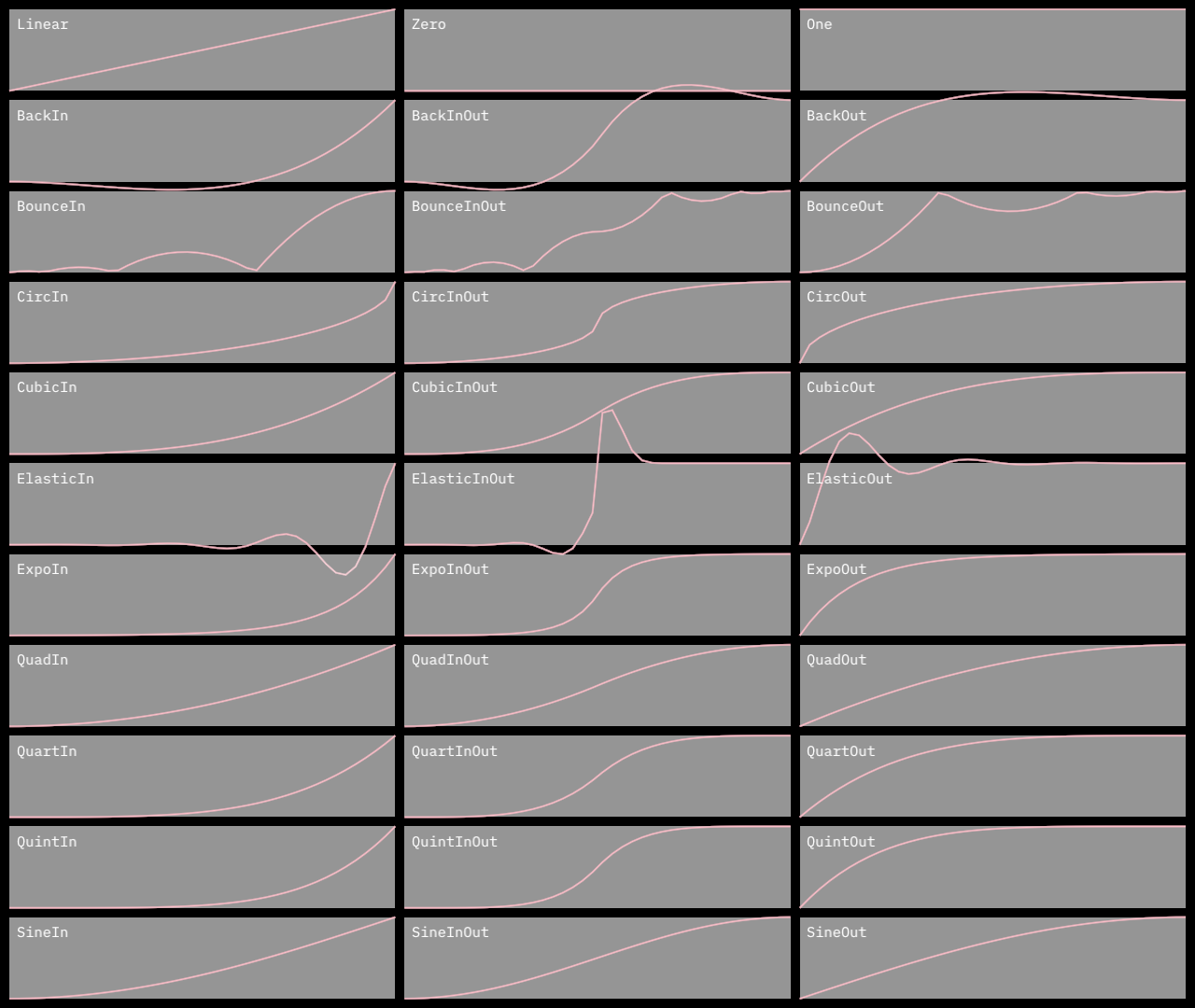
| type | |
|---|---|
| linear | easeLinear |
| constant 0 | easeZero |
| constant 1 | easeOne |
| type | in | in out | out |
|---|---|---|---|
| quad | easeQuadIn |
easeQuadInOut |
easeQuadOut |
| cubic | easeCubicIn |
easeCubicInOut |
easeCubicOut |
| quart | easeQuartIn |
easeQuartInOut |
easeQuartOut |
| quint | easeQuintIn |
easeQuintInOut |
easeQuintOut |
| circ | easeCircIn |
easeCircInOut |
easeCircOut |
| expo | easeExpoIn |
easeExpoInOut |
easeExpoOut |
| sine | easeSineIn |
easeSineInOut |
easeSineOut |
| back | easeBackIn |
easeBackInOut |
easeBackOut |
| bounce | easeBounceIn |
easeBounceInOut |
easeBounceOut |
| elastic | easeElasticIn |
easeElasticInOut |
easeElasticOut |
Usage
fun easeX(
t: Double, // current time
b: Double = 0.0, // beginning (output value when t is 0.0)
c: Double = 1.0, // change (output delta)
d: Double = 1.0 // duration = end time
)
The most common usage involves repeatedly calling the easing function increasing
the t argument while keeping other arguments unchanged. When t increases from 0.0 up to d, the returned value slides from b to b + c.
Example
For accelerating from 40.0 down to 10.0 in 10 steps:
repeat(10) {
val y = easeQuadIn(it.toDouble(), 40.0, -30.0, 9.0)
println("$it -> $y")
}
Outputs
0 -> 40.0
1 -> 39.629629629629626
2 -> 38.51851851851852
3 -> 36.666666666666664
4 -> 34.074074074074076
5 -> 30.74074074074074
6 -> 26.666666666666668
7 -> 21.85185185185185
8 -> 16.2962962962963
9 -> 10.0
Note how most result values are closer to 40.0 than to 10.0, due to the usage of
an In easing function. easeCubicIn, easeQuartIn and easeQuinticIn functions would make this even more obvious.
Default arguments
When t is in [0, 1] we can omit most arguments
val e0 = easeQuadIn(t, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0)
val e1 = easeQuadIn(t)
Using the Easing enumeration
The Easing enum contains all easing functions.
val et = Easing.QuadIn.function(t, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0)
// list all easing function names
Easing.values().forEach { easing ->
println(easing.name)
}
// find out how many easing functions are available
println(Easing.values().size)
Demos
DemoEasings01
Visualizes Easing types as a graph and as motion.
[grid] is used to layout graphs on rows and columns.