100 lines
2.8 KiB
Markdown
100 lines
2.8 KiB
Markdown
# orx-easing
|
|
|
|
Easing functions for smooth animation or non-linear interpolation.
|
|
|
|
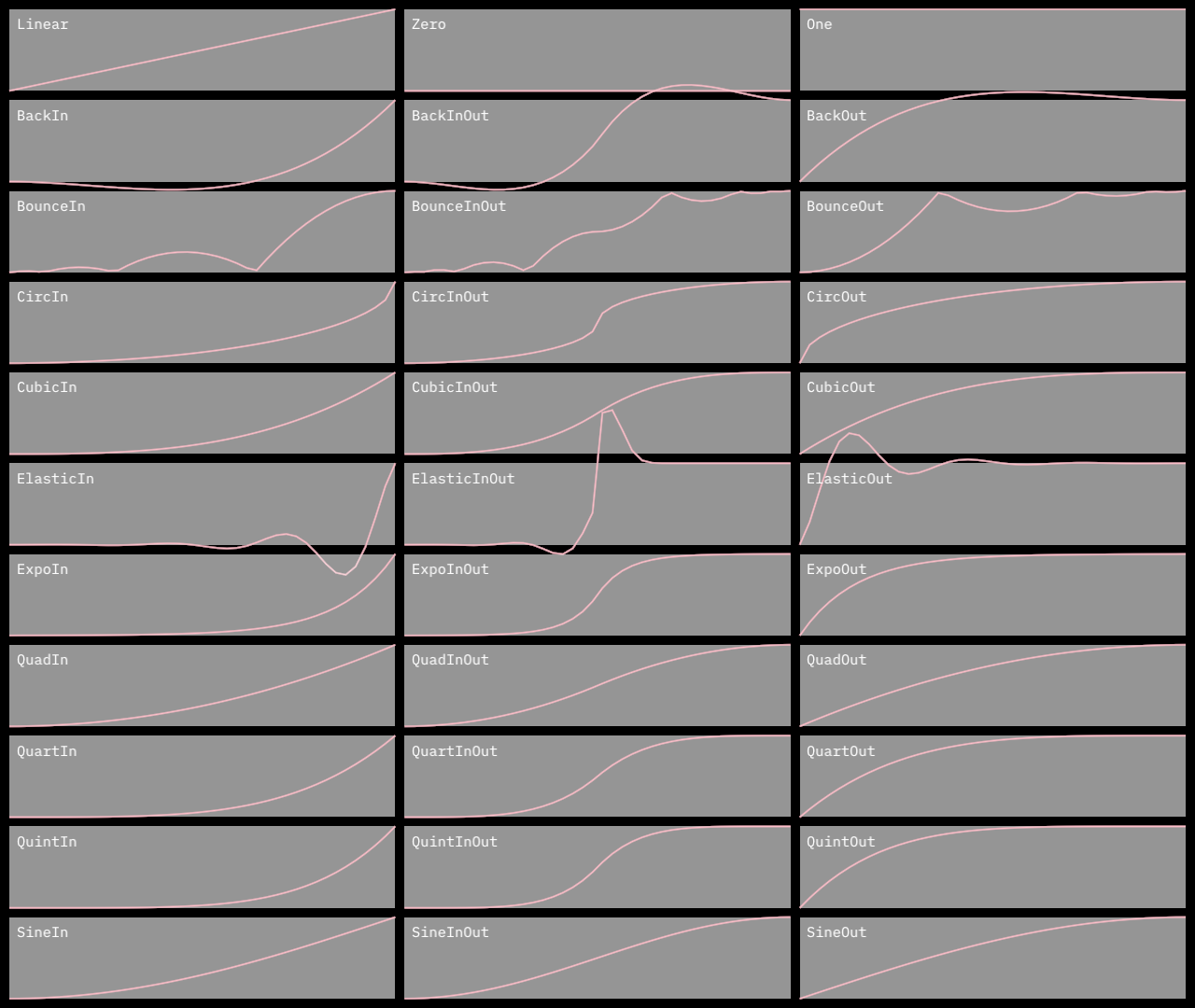
Similar to those on https://easings.net
|
|
|
|
| type | |
|
|
|:-----------|:-------------|
|
|
| linear | `easeLinear` |
|
|
| constant 0 | `easeZero` |
|
|
| constant 1 | `easeOne` |
|
|
|
|
| type | in | in out | out |
|
|
|---------|----------------:|-------------------:|-----------------:|
|
|
| quad | `easeQuadIn` | `easeQuadInOut` | `easeQuadOut` |
|
|
| cubic | `easeCubicIn` | `easeCubicInOut` | `easeCubicOut` |
|
|
| quart | `easeQuartIn` | `easeQuartInOut` | `easeQuartOut` |
|
|
| quint | `easeQuintIn` | `easeQuintInOut` | `easeQuintOut` |
|
|
| circ | `easeCircIn` | `easeCircInOut` | `easeCircOut` |
|
|
| expo | `easeExpoIn` | `easeExpoInOut` | `easeExpoOut` |
|
|
| sine | `easeSineIn` | `easeSineInOut` | `easeSineOut` |
|
|
| back | `easeBackIn` | `easeBackInOut` | `easeBackOut` |
|
|
| bounce | `easeBounceIn` | `easeBounceInOut` | `easeBounceOut` |
|
|
| elastic | `easeElasticIn` | `easeElasticInOut` | `easeElasticOut` |
|
|
|
|
## Usage
|
|
|
|
```kotlin
|
|
fun easeX(
|
|
t: Double, // current time
|
|
b: Double = 0.0, // beginning (output value when t is 0.0)
|
|
c: Double = 1.0, // change (output delta)
|
|
d: Double = 1.0 // duration = end time
|
|
)
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The most common usage involves repeatedly calling the easing function increasing
|
|
the `t` argument while keeping other arguments unchanged. When `t` increases from 0.0 up to `d`, the returned value slides from `b` to `b + c`.
|
|
|
|
### Example
|
|
|
|
For accelerating from 40.0 down to 10.0 in 10 steps:
|
|
|
|
```kotlin
|
|
repeat(10) {
|
|
val y = easeQuadIn(it.toDouble(), 40.0, -30.0, 9.0)
|
|
println("$it -> $y")
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Outputs
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
0 -> 40.0
|
|
1 -> 39.629629629629626
|
|
2 -> 38.51851851851852
|
|
3 -> 36.666666666666664
|
|
4 -> 34.074074074074076
|
|
5 -> 30.74074074074074
|
|
6 -> 26.666666666666668
|
|
7 -> 21.85185185185185
|
|
8 -> 16.2962962962963
|
|
9 -> 10.0
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Note how most result values are closer to 40.0 than to 10.0, due to the usage of
|
|
an `In` easing function. `easeCubicIn`, `easeQuartIn` and `easeQuinticIn` functions would make this even more obvious.
|
|
|
|
### Default arguments
|
|
|
|
When `t` is in `[0, 1]` we can omit most arguments
|
|
|
|
```kotlin
|
|
val e0 = easeQuadIn(t, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0)
|
|
val e1 = easeQuadIn(t)
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Using the `Easing` enumeration
|
|
|
|
The `Easing` enum contains all easing functions.
|
|
|
|
```kotlin
|
|
val et = Easing.QuadIn.function(t, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0)
|
|
|
|
// list all easing function names
|
|
Easing.values().forEach { easing ->
|
|
println(easing.name)
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// find out how many easing functions are available
|
|
println(Easing.values().size)
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
<!-- __demos__ -->
|
|
## Demos
|
|
### DemoEasings01
|
|
[source code](src/jvmDemo/kotlin/DemoEasings01.kt)
|
|
|
|
|